Limit business rules determine a price range with a maximum and a minimum that will cap the price advice given. This ensures Omnia never prices a product outside of your preferred range.
To set a limit business rule, you first need to define the limit actions that form that rule. You have three limit actions to choose from:
- Cap recommended price point to competitors
- Cap recommended price point to connect field
- Cap recommended price point to a certain position in the market
In this article we will explain the differences between these actions.
Cap recommended price point to competitors
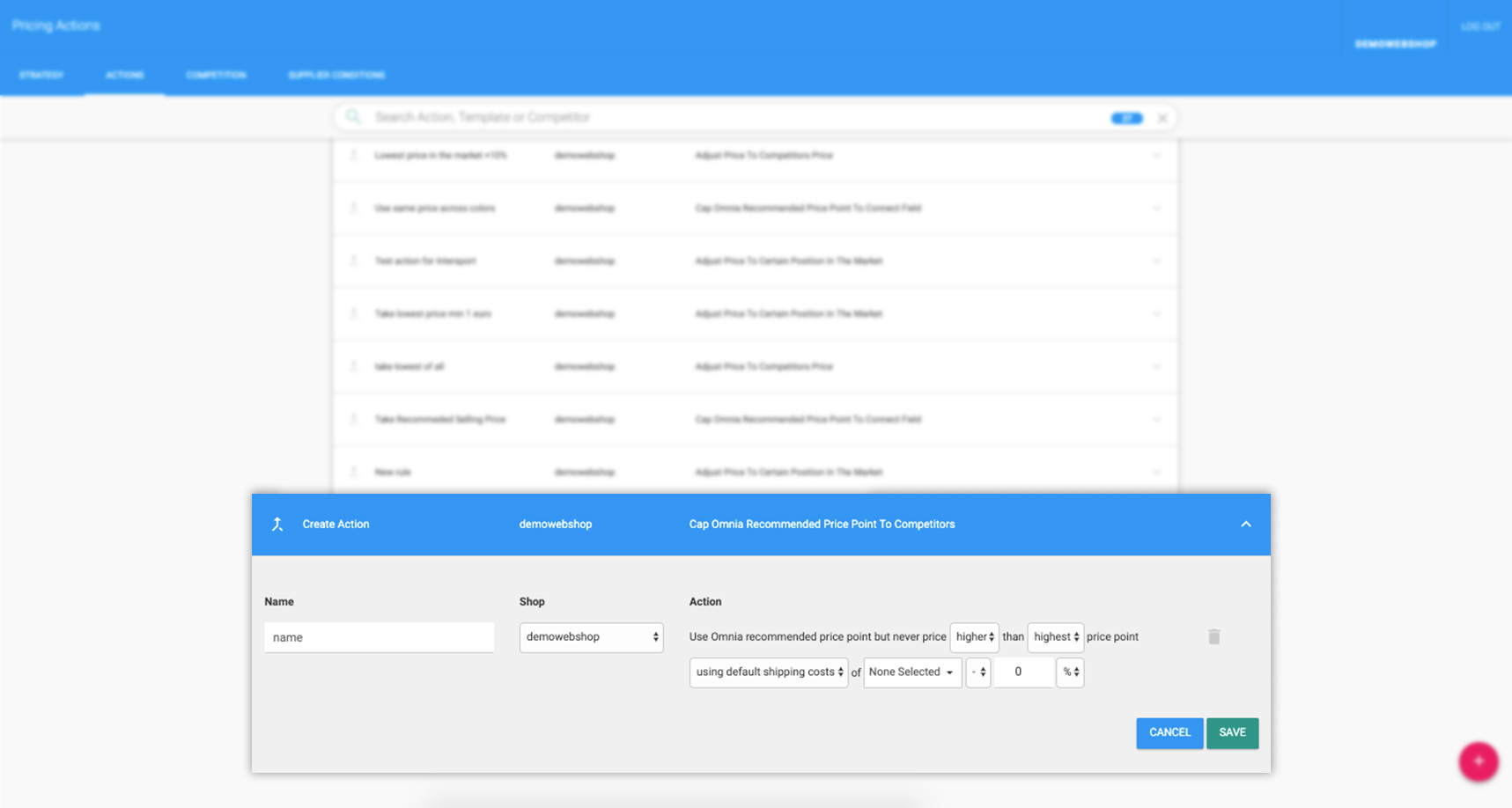
With this action, you use Omnia's recommended price point, but you restrict the price according to the prices of selected competitors.
To set this rule, use the form fields to decide…
- Whether you want to limit yourself higher or lower than a certain price point
- Whether the limiting price point is the highest or lowest price point on the market
- If you want to include or exclude shipping costs
- If you want to select certain competitors
- By how much you want to limit your price points (plus or minus a certain number of percentage points or euros)
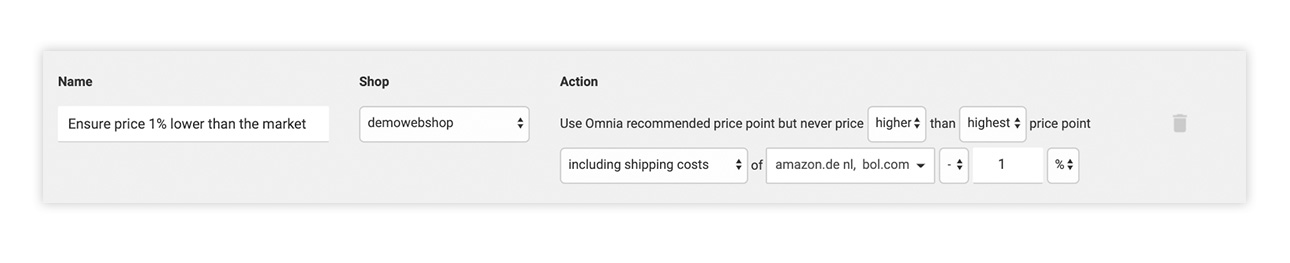
Example:
You want to make sure that your price is always below the highest price point of your most important competitors (e.g. Amazon and bol.com).
In Omnia, the logic reads as: ”Use Omnia recommended price point but never price higher than highest price point including shipping costs of Amazon.de NL, bol.com, -1%.”
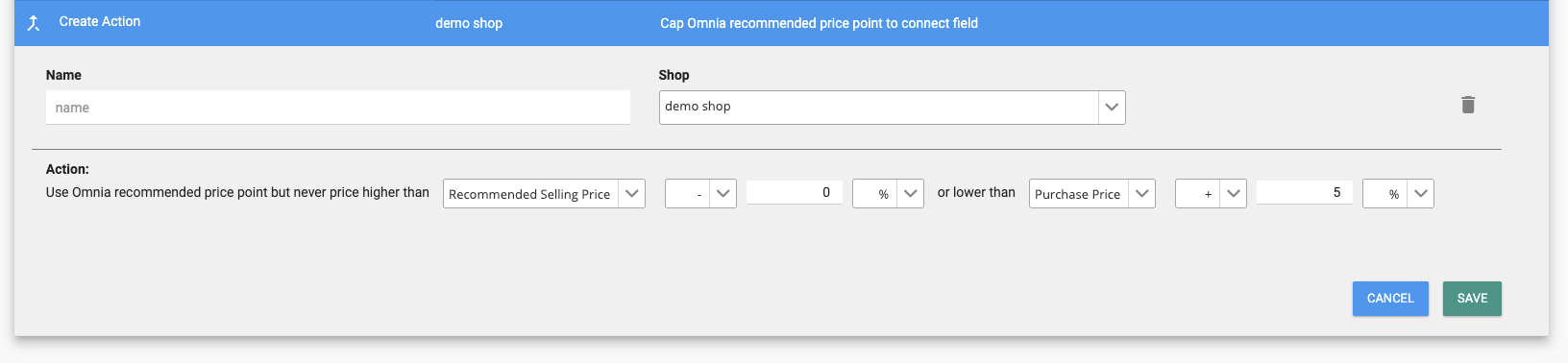
Cap recommended price point to connect field
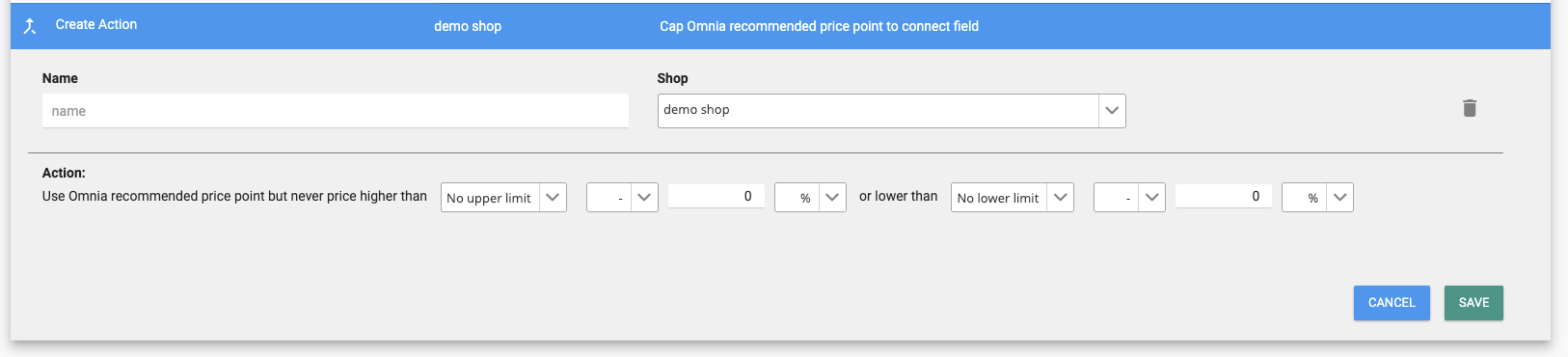
With this action, you use Omnia's recommended price point, but you restrict the price according to a connect field. Connect fields are any internal data points that you configured in the import mapping, such as purchase price or the recommended selling price (see article).
You can select whether you want to use connect fields as a limit. Just click on the drop down menu and select from the options available. Additionally, you can fill in an adjustment of the connect field that you selected. For example: you can take the purchase price + 10% as a lower limit.
You also have the option to set no upper or lower limits. These options are also available in the drop-down menu.
Example:
You want to make sure that your price is never higher than the recommended selling price and never lower than 5% above the purchase price.
In Omnia, this logic reads as: “Use Omnia recommended price point but never price higher than Recommended Selling Price or lower than Purchase Price +5%”
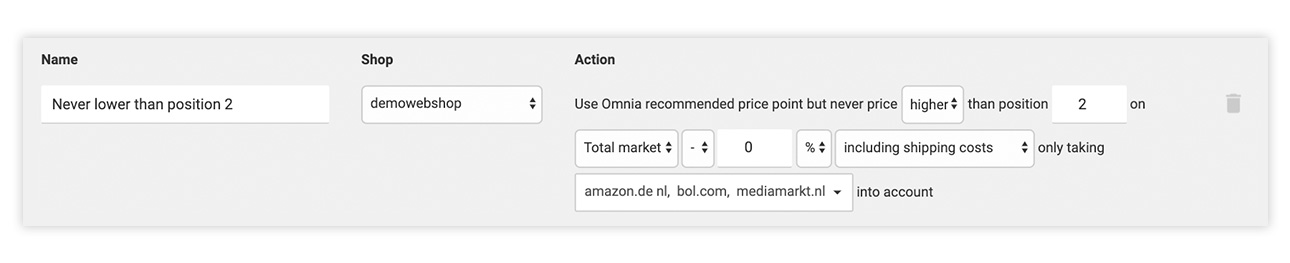
Cap recommended price point to a certain position in the market
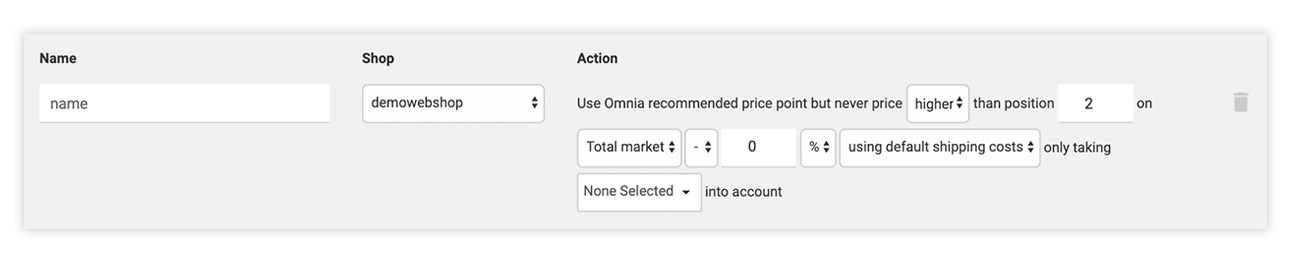
With this action, you use Omnia's recommended price point, but you restrict the price according to the position in the market. You can also choose to account for selected competitors.
To set this rules, use the form fields to decide
- Whether you will price higher or lower than the competitor in a certain position
- Which position to use as the limiter
- What data source you will use
- What percentage or euro amount you want to be the difference
- Whether to include or exclude shipping costs
- Which competitors to consider
Example:
You want to make sure that your price is always at least position 2 between Amazon, bol.com and Mediamarkt.
In Omnia, this logic reads as: “Use Omnia recommended price point but never price higher than position 2 on Total market -0% including shipping costs and only taking amazon.de, bol.com, and mediamarkt.nl into account